Investigation of the added value of 3D segmented CT images to the classification accuracy of proximal humeral fractures (FractSeg)
Goal
To investigate the feasibility and added value of semi-automatic segmented 3D CT visualizations in proximal humeral fracture classification for observers with two different experience levels: residents and specialized shoulder surgeons.
Results
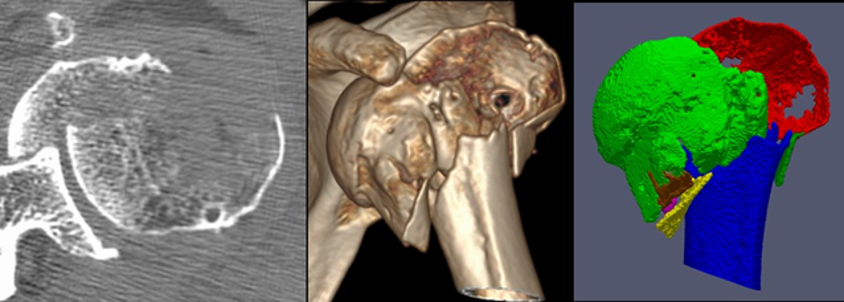
Seventeen patients with proximal humeral fractures and a preoperative CT scan were included in this retrospective study. The CT scans were semi-automatically segmented, indicating every fracture fragment in a different color. Fracture classification ability of 21 orthopedic residents and 12 experienced shoulder surgeons was tested. Both groups were asked to classify the fractures using 3 different modalities (standard slice-wise CT analysis, conventional 3D CT reconstruction, and 3D segmented model) into three different classification systems (Neer, AO and LEGO). All participants were able to classify the fractures significantly better using the 3D segmentations (94% correct answers on average) compared with the conventional 3D reconstructions (54%) and with the standard slice-wise CT analysis (35%) into the three classification systems, p<0.01. Both observer groups achieved significantly worse classification accuracy in the LEGO system compared to the two others.
-
Partner
Putzeys G (MD), AZ Groeninge Hospital Kortrijk, Belgium
Nijs S (Prof), University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium